Create a Project Distribution
Introduction
Goal
Package your project as a distribution that is ready to be deployed in a Tomcat installation in an environment.
Background
At the end of a development iteration you need to be able to package your project and deploy it to a test, an acceptance and eventually a production server. If you have set up your project with the Maven archetype, creating a project distribution for Tomcat works out of the box. This page explains how to create such a distribution.
Deployment Diagram
Below is a diagram that depicts the structure of the deployment we are aiming at.
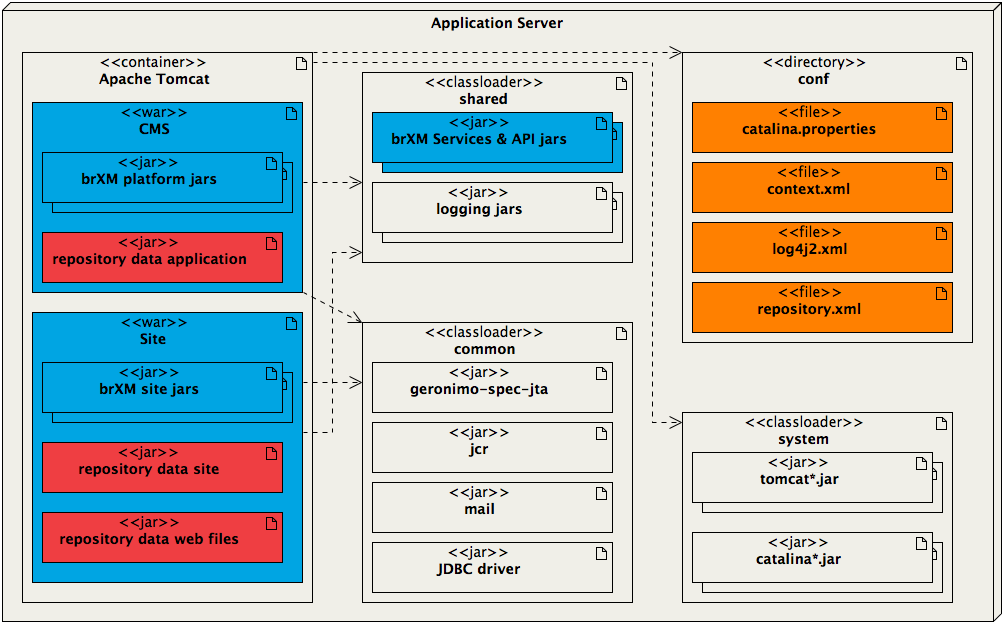
(Legend: blue = brXM out-of-the-box, light grey = third party, red = project-specific, orange = environment-specific)
- Apache Tomcat container
Two war files are deployed in the Tomcat container (${catalina.base}/webapps/):- CMS
cms.war contains the brXM platform webapp as well as the repository-data-application module packaged as jar file. The repository data jar is used to bootstrap application configuration into the repository during the first deployment, and optionally on subsequent deployments depending on the deployment settings. - Site
site.war contains the brXM site webapp and the repository-data-site and repository-data-webfiles modules packaged as jar files (from which site configuration and web files are bootstrapped into the repository).
- CMS
-
Common classloader
${catalina.base}/common/lib/ is the location of container-wide artifacts. These will be loaded by Tomcat's common classloader. - Shared Classloader
${catalina.base}/shared/lib is the location where Tomcat's shared classloader will load artifacts from. This classloader is shared between all deployed web applications and enables communication between them. The CMS and Site webapps communicate with each other through the brXM Services and API jars deployed in the shared classloader.
When creating a distribution with development data, the repository-data-development and repository-data-site-development jars are also added to ${catalina.base}/shared/lib. - Configuration Directory
Finally ${catalina.base}/conf is where environment-specific configuration can be put. For example, a development environment will typically use a different database configuration than a production environment and so the project distribution might not deliver the configuration settings specific to the production environment. Those can be configured here.
However, please note that common libraries (in common) and environment-specific configuration (in conf) are typically configured at container level (e.g. see Configure the Application Server (Apache Tomcat on Linux)). When deploying a distribution in such an environment, only the webapps and shared directories (blue in the diagram above) should be unpacked. The deployment instructions reflect this.
Create a Project Distribution
A standard Bloomreach Experience Manager project based the Maven archetype provides two profiles in its root POM file which configure the Maven Assembly Plugin that is used to create a distribution:
- dist to create a distribution without development data
- dist-with-development-data to create a distribution with development data
Whether you need a distribution with or without development data depends on your use case. Deploying for the first time in a new ("empty") environment may require a distribution with development data in order to seed some content. Subsequent deployments typically don't need any development data to be bootstrapped, unless specifically required by the project release being deployed.
Create a Project Distribution without Development Data
To create a distribution without development data, run the following commands in the project's root directory:
mvn clean verify mvn -P dist
A tar.gz distribution file has now been created in the target directory of the main project and contains the following files for brXM 16.0.0:
$ tar -tf target/myproject-0.1.0-SNAPSHOT-distribution.tar.gz common/lib/angus-activation-2.0.2.jar common/lib/angus-mail-2.0.3.jar common/lib/geronimo-jta_1.1_spec-1.1.1.jar common/lib/jakarta.activation-api-2.1.3.jar common/lib/jakarta.mail-api-2.1.3.jar common/lib/jcr-2.0.jar conf/context.xml conf/log4j2.xml shared/lib/hippo-cms7-commons-16.0.0.jar shared/lib/hippo-repository-api-16.0.0.jar shared/lib/hippo-repository-builtin-16.0.0.jar shared/lib/hippo-services-16.0.0.jar shared/lib/hst-api-16.0.0.jar shared/lib/jcl-over-slf4j-1.7.36.jar shared/lib/log4j-api-2.23.1.jar shared/lib/log4j-core-2.23.1.jar shared/lib/log4j-slf4j-impl-2.23.1.jar shared/lib/slf4j-api-1.7.36.jar webapps/cms.war webapps/site.war
Note on shared/lib: some out-of-the-box features will add jars to it, for instance the relevance module.
Here are two web applications packaged as war files inside a directory called webapps, a number of libraries in a directory called shared/lib, another set in a directory called common/lib, and some configuration files such as a log4j descriptor and a Tomcat context descriptor in the conf directory. This is the directory layout Tomcat uses to load the different artifacts your project delivers. Simply unpacking this distribution in the root directory of a Tomcat installation will put these artifacts in the correct locations.
For brXM 15.6 and lower the list is very similar although the versions vary. The common/lib does differ because from v15 to v16 Angus mail/activation is used rather than Sun mail:
$ tar -tf target/myproject-1.0.0-distribution.tar.gz common/lib/jakarta.mail-1.6.7.jar // (jakarta.activation.jar is to be provided) common/lib/jcr-2.0.jar common/lib/geronimo-jta_1.1_spec-1.1.1.jar conf/context.xml conf/log4j2.xml shared/lib/hippo-cms7-commons-15.6.0.jar shared/lib/hippo-repository-api-15.6.0.jar shared/lib/hippo-repository-builtin-15.6.0.jar shared/lib/hippo-services-15.6.0.jar shared/lib/hst-api-15.6.0.jar shared/lib/jcl-over-slf4j-1.7.30.jar shared/lib/log4j-api-2.17.1.jar shared/lib/log4j-core-2.17.1.jar shared/lib/log4j-slf4j-impl-2.17.1.jar shared/lib/slf4j-api-1.7.30.jar webapps/cms.war webapps/site.war
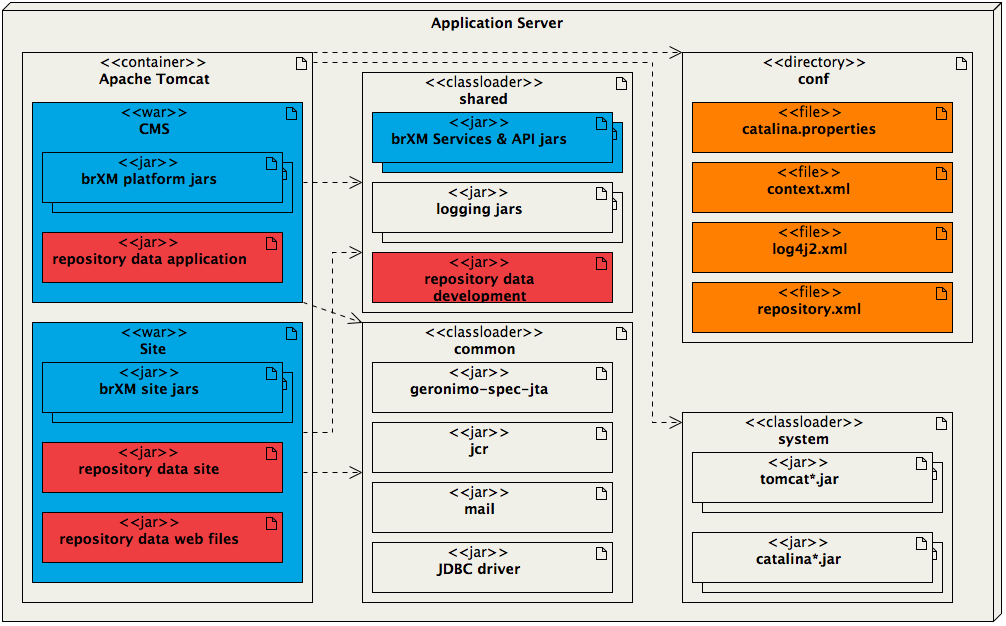
Create a Project Distribution with Development Data
To create a distribution with development data, run the following commands in the project's root directory:
mvn clean verify mvn -P dist-with-development-data
A tar.gz distribution file has now been created in the target directory of the main project and contains the same files as a distribution without development data, with the addition of the following file (assuming project name myproject and project version 1.0.0):
shared/lib/myproject-repository-data-development-1.0.0.jar shared/lib/myproject-repository-data-site-development-1.0.0.jar
The deployment diagram then looks as follows:
Customization
Internally the Maven Assembly Plugin is configured by an assembly descriptor. This descriptor is located at src/main/assembly/distribution.xml, and includes a number of assembly component descriptors.
The file looks like this:
<assembly xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/plugins/maven-assembly-plugin/assembly/1.1.2" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/plugins/maven-assembly-plugin/assembly/1.1.2 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/assembly-1.1.2.xsd"> <id>distribution</id> <formats> <format>tar.gz</format> </formats> <includeBaseDirectory>false</includeBaseDirectory> <componentDescriptors> <componentDescriptor>conf-component.xml</componentDescriptor> <componentDescriptor>webapps-component.xml</componentDescriptor> <componentDescriptor>common-lib-component.xml</componentDescriptor> <componentDescriptor>shared-lib-component.xml</componentDescriptor> </componentDescriptors> </assembly>
If you have custom needs, such as an additional web application or a shared library you want packaged, modify the descriptors to your liking. Most cases should be self-explanatory by looking at the contents of the provided descriptors. For instance, to package an additional shared artifact you would add an <include> element with the groupId:artifactId coordinates of that artifact next to the dependency set defined in the shared-lib-component.xml descriptor. Make sure that it is in fact defined as a provided-scoped dependency in your POM or the assembly plugin won't be able to resolve the artifact.
Another common use case involves having to package a container-wide artifact for deployment to ${catalina.base}/common/lib, so that it will be loaded by Tomcat's common class loader. This is for instance the case with JDBC drivers that you want to configure as a JNDI DataSource in Tomcat. You can achieve this by adding the additional dependency to the common-lib-component.xml descriptor. For example to also packages the MySQL driver, add the following include to the dependency set:
<include>com.mysql:mysql-connector-j</include>
Again, your projects primary POM descriptor must define this artifact as a provided dependency.
If you have requirements beyond this, refer to the Maven Assembly Plugin descriptor documentation here.

