Monitor Application Logs using Humio
Introduction
Goal
Use Humio to monitor log files for the CMS and Site applications running in your Bloomreach Cloud environments.
Background
Bloomreach Cloud uses the external service humio.com to expose the application logs of the CMS and Site applications running in the environments.
This page provides basic directions for accessing your application logs. More learning resources can be found at https://docs.humio.com/.
Access Humio
As a Bloomreach Cloud customer, you must provide Bloomreach a GitHub or Bitbucket account to sign in to Humio. Bloomreach will add this account to the Humio repo as a user. If you do not have a GitHub or Bitbucket account, please contact Helpdesk for a workaround.
Log in at https://cloud.humio.com/ using the credentials you provided to Bloomreach. For example when using a GitHub account, click on Log in with GitHub and enter your credentials.
The first time you log in to Humio, you'll have to go through some additional steps:
- Fill in the profile form.
- Choose the free account.
- Follow or skip the tutorial.
Once logged in, you will see two options on the Repositories and Views tab: your stack and your sandbox:
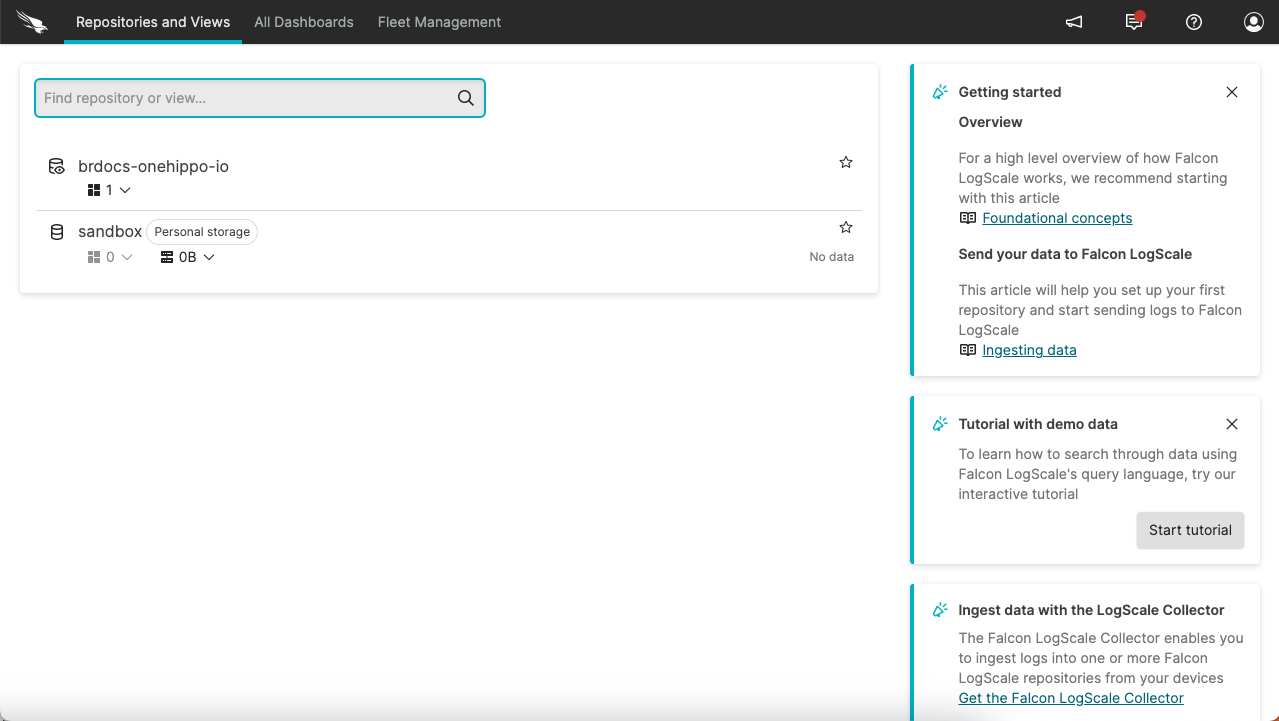
Click on the name of your stack. In the bottom left you will see fields appear that you can use for filtering.
Create Filters for Your Environments
Application logs for all your Bloomreach Cloud environments are collected in the same Humio instance. Therefore, it's a good idea to create a search filter for each of your environments.
For example, for an environment called "blue", select "environment" in the list of fields and click on the Match value in query for the "blue" value.
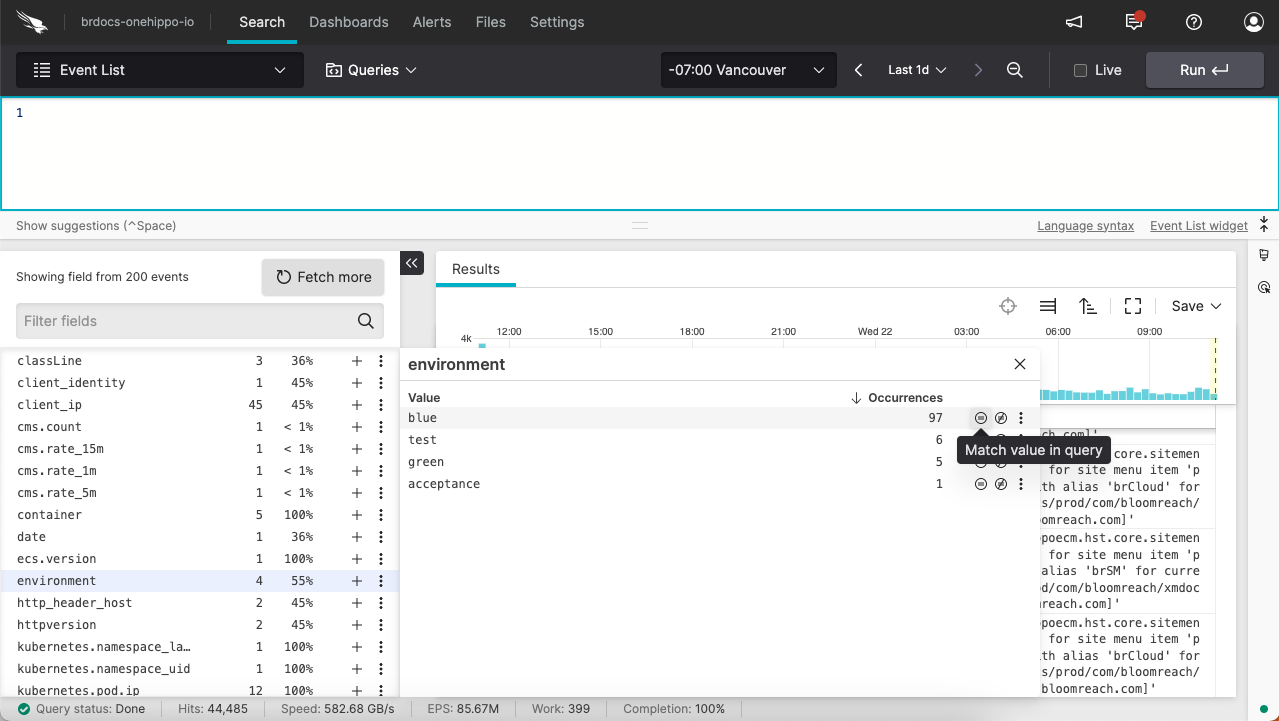
Alternatively, enter the following query in the search box:
environment=blue
Click on the Run button to execute the search.
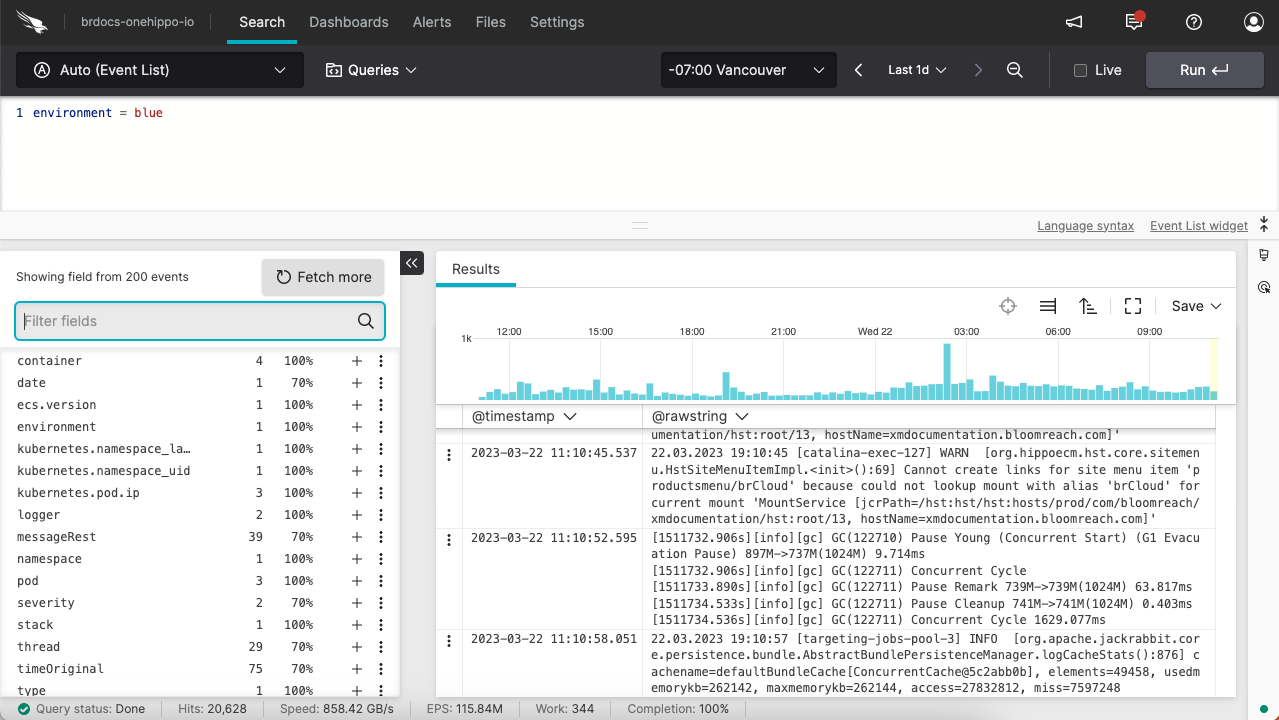
To save the search, open the Save dropdown (at the top right of the logs) and select Saved Query.
Select a Time Range
In the top right you can see the currently selected time range. By default, this is Last 1d. Click on it to select a different time range. Use the live-query checkbox to get a live tail.
Select Fields to Display
Log entries have a number of different fields. If you click on a row, you will see the fields. Some interesting fields are:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| class | The Java class in which the log entry originated. |
| container | Log entries are separated into different containers by type. Available containers are cms-log, site-log, and audit-log. |
| environment | Name of the Bloomreach Cloud environment from in which the log entry originated. For example, blue or green. |
| severity | Severity or log level of the message, for example INFO, WARNING, or ERROR. |
| stack | Name of the Bloomreach Cloud stack in which the log entry originated. For example, mycloud.onehippo.io. Only interested if you are managing more than one stack. |
Create Alerts for your Environments
Humio has support for alerting and can be configured to notify external systems about error conditions or other events. See Automation and Alerts in the Humio docs for instructions.
It's recommended to create an alert for Out of Memory exceptions. See Monitor and Analyze JVM Memory for details.

