Document Type Editor
Introduction
Bloomreach Experience Manager includes a WYSIWYG Document Type Editor which allows web developers to create and modify document types to be used in their projects. A document type defines a type's data structure as well as the editing template used by authors to create and modify documents of that type.
Using the Document Type Editor
When working with content types, please be aware of the reserved names in the Delivery API and avoid using these names in your content types!
The Document Type Editor is available to users with administrator privileges and is located in the Content Workspace in the Document Types section.
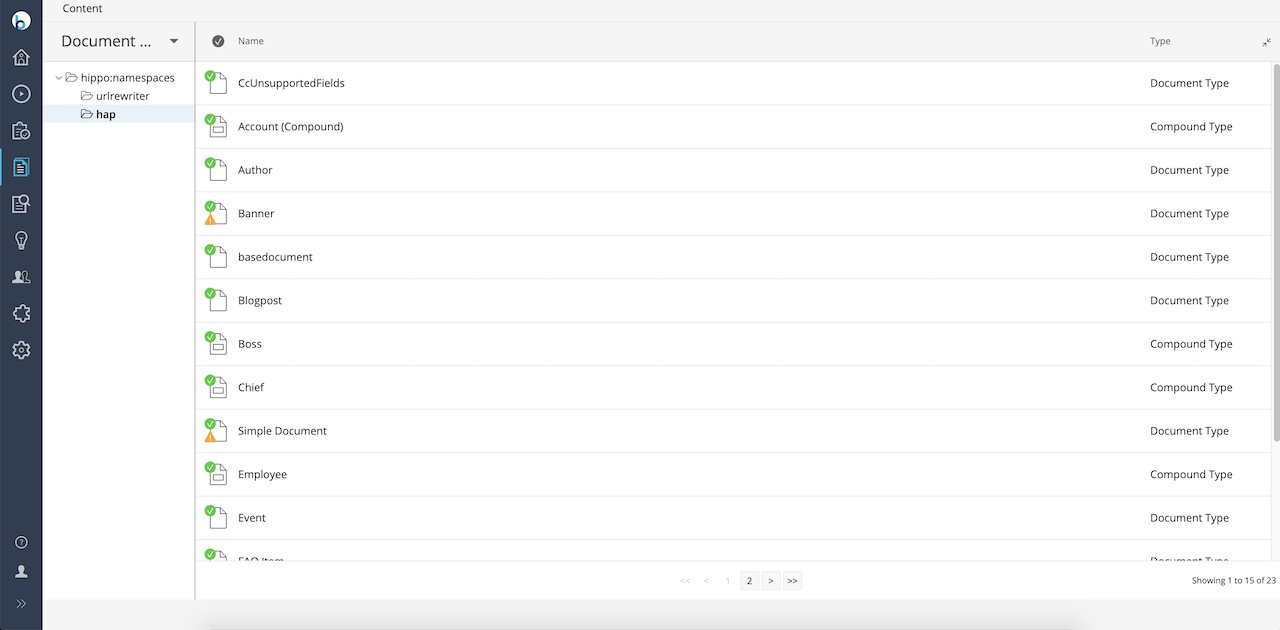
Browsing, creating and editing document types is very similar to browsing, creating and editing actual documents.
When editing a document type fields can be added, moved, modified and removed.
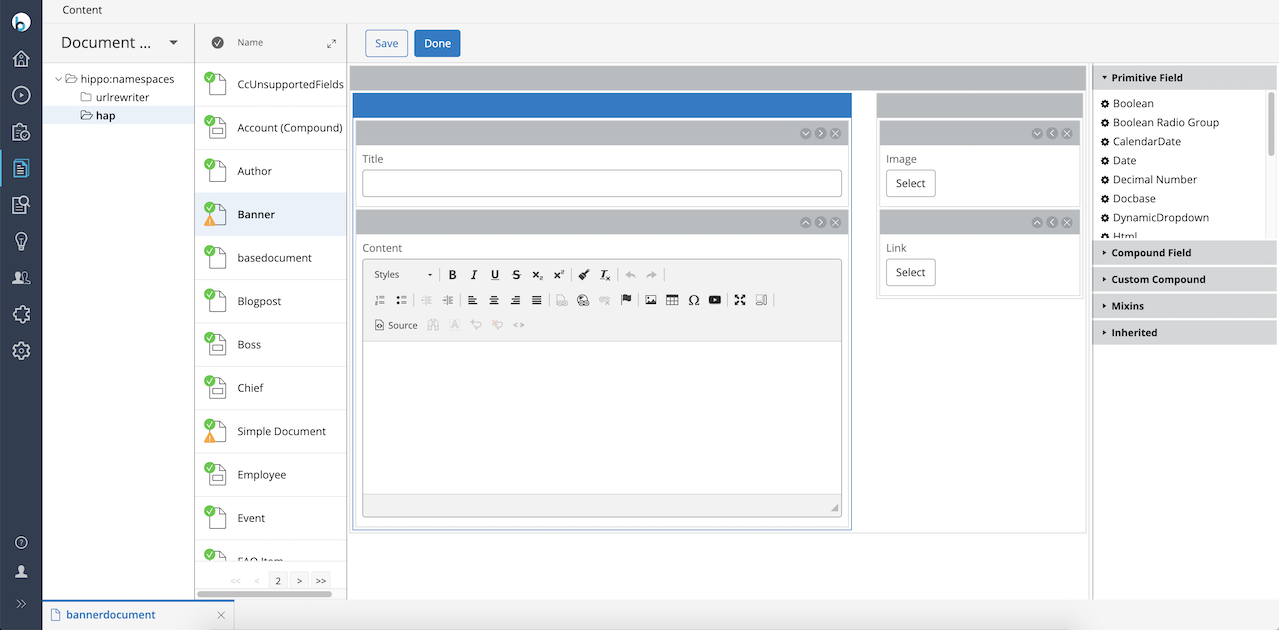
A new or modified document type must be committed before it is available to authors.
Standard Field Types
Bloomreach Experience Manager provides a standard set of field types that can be used to create document types. Additional field types can be added through plugins or custom development.
Primitive Types
Primitive Types are field types that translate directly to primitive JCR property types.
Boolean
A Boolean field is displayed as a single checkbox. Its value is either true (checked) or false (unchecked). Its default value if false.

Boolean Radio Group
A single value radio button group widget to set a Boolean value. Its default value is false. Optionally, the labels for the true and false options can be read from a value list document.

CalendarDate
A CalendarDate allows a date to be entered in a text box or through the provided calendar widget.
Date
A Date field includes date as well as time. A date value can be entered in a text box or through the provided calendar widget. A time value can be entered through text boxes for hours and minutes.
Decimal Number
A Decimal Number field is used for decimal values. Its default value is 0.0.
Docbase
A Docbase field is used to create a weak reference to a folder, document, asset or image in the repository. It stores the UUID of the referenced item's JCR node in a String property.
Dynamic Dropdown
A single value dropdown widget populated from a value list service.
Html
A Html field is used for formatted text content. It is stored as HTML markup in a String property.
Open UI String
An Open UI String field uses the document field extension point to display a custom field type.
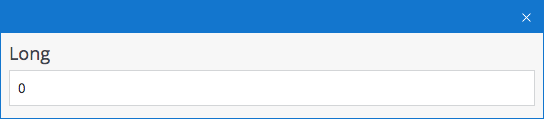
Integer Number
A Long field is used for integers (or whole numbers). Its default value is 0.
Radio Group
A single value radio button group widget populated from a value list service.

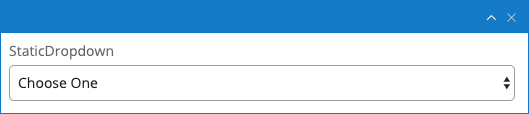
Static Dropdown
A single value dropdown widget populated from a static value list specified as comma-separated values in the field properties.
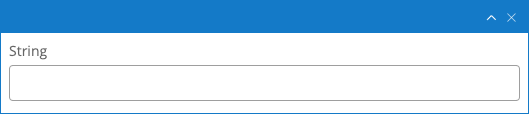
String
A String field is used for single-line plain text content.
Taxonomy
A Taxonomy field is used to select categories from a taxonomy. The taxonomy must be an existing taxonomy, created earlier from Essentials or from the console app and is referred by its JCR node name in the field's taxonomy.name property. See Taxonomy Plugin Configuration for details.

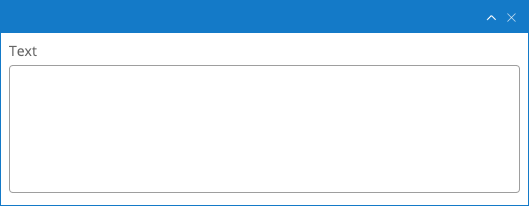
Text
A Text field is used for multi-line plain text content. It is stored as a String property.
Compound Types
Compound Types are reusable blocks of fields. They are stored as child nodes. A Compound Type can contain both Primitive and Compound Type fields.
Image Link
An Image Link field is used to include an image from the gallery in the document. It is stored as a reference to the actual JCR node in which the image is stored. The delivery tier will resolve the reference and translate it to a website URL on-the-fly. If a CMS user tries to delete the referenced image they will see a warning that it is being referred to and deleting the image will cause a broken link in the referring document.

Link
A Link field is used to create an internal link to a different content item (such as a document or asset) in the repository. It is stored as a reference to the actual JCR node in which that content item is stored. The delivery tier will resolve the reference and translate it to a website URL on-the-fly. If a CMS user tries to delete the referenced content item they will see a warning that it is being referred to and deleting the item will cause a broken link in the referring document.

Resource
A Resource field is used to embed a file (e.g. an image or a PDF document) in a document. The file is physcially stored inside a JCR node in the document and can't be reused by other documents.

Rich Text Editor
A Rich Text Editor field is used to store fully featured rich text content. It is stored as HTML markup inside a JCR node in the document. The Rich Text Editor provides authors with the freedom to format text and include tables, images, links, etc. The delivery tier must parse rich text content in order to resolve references to other content items (such as images and links to other documents).
Value List Item
A key-value compound type that is part of the Value List document type used to manage values for Selection fields such as Dynamic Dropdowns and Radio Groups.
Field Properties
Each field in a document type has a number of properties. The exact properties differ per field type, but every field must at least have a Caption property and a Path property.
Caption
The caption of a field is the label that is displayed directly above the field in the editing template. Authors will know a field by its caption. A caption is single-line plain text and may contain spaces and special characters.
Path
The path of a field is the name that is used to store the value of the field under. Under the hood the system exclusively refers to a field by its path (prefixed by a namespace). It translates directly to a JCR property name (in case of a primitive type) or node name (in case of a compound type). A path may not contain spaces or special characters.
Hint
Optionally a hint to authors can be added to a field. The hint is displayed as a question mark with a mouseover popup.
CSS Classes
Optionally one or more CSS classes can be added in order to apply custom styling to the field. The actual CSS classes must be defined in a custom .css file included in the cms module of the project.
Required
Any field that is not Optional can be made required by checking the Required checkbox. Authors can't save documents if they haven't entered a value in a required field.
Optional
Any field that is not Required and not Multiple can be made optional by checking the Optional checkbox. Authors can remove the field completely from a document by clicking on an 'X' icon, and add it back by clicking on a '+' icon. This can be particularly useful for compound fields that contain required fields.
Multiple and Ordered
Any field that is not Optional can be made multi-valued by checking the Multiple checkbox. This adds plus and minus icons to the field so authors can add or remove values.
A multi-valued field can be made orderable by checking the Ordered checkbox. This adds arrow icons to the field so authors can move values up, down, to the top, and to the bottom. Optionally, the "move to the top" and "move to the bottom" arrows can be hidden by adding the CSS class hide-top-bottom-arrows to the field's CSS Classes property.
Custom Validation
In addition to defining fields as required (see above), it's possible to create custom field validators.
Document Type Inheritance
Bloomreach Experience Manager supports document type inheritance. A project created using the archetype always contains a base document type from which all other document types inherit. This is the default super type when creating a new document.
You can choose to make a new document type inherit from a different document type by selecting one in the Super type field in the New document type dialog:
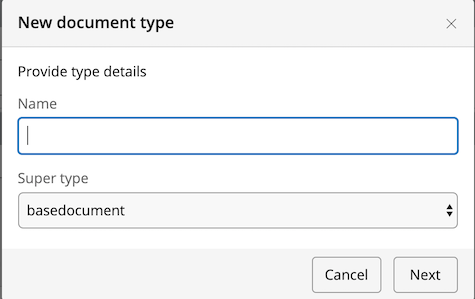
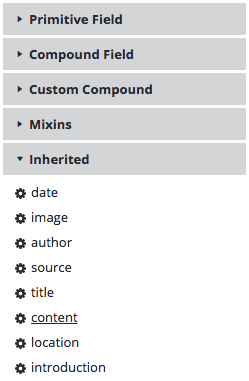
The new document type's editing template will initially be empty. The fields inherited from the super type can be manually added to the template by choosing them from the Inherited section in the right column of the editor: